Google Updated Its How Google Search Works Page in June 2020
Posted On : June 27th, 2020 By : Diptimayee Mohanty To : Google Search TipsGoogle has updated its “How Google Search Works” page this week with new content in both short version as well as in long version.
“How Google Search Works” page has mainly three sections- crawling, indexing & serving (ranking). But major changes you can see only in the crawling section, with a little change in the indexing section and no change in serving (ranking) section.
We know Google makes updates in these types of pages, but this time we are seeing some big changes in content in this page. Recently added content are marked with red outlines in the screenshot below.
New Contents In The Short Version:
First of all we’ll discuss about the new contents in the short version.
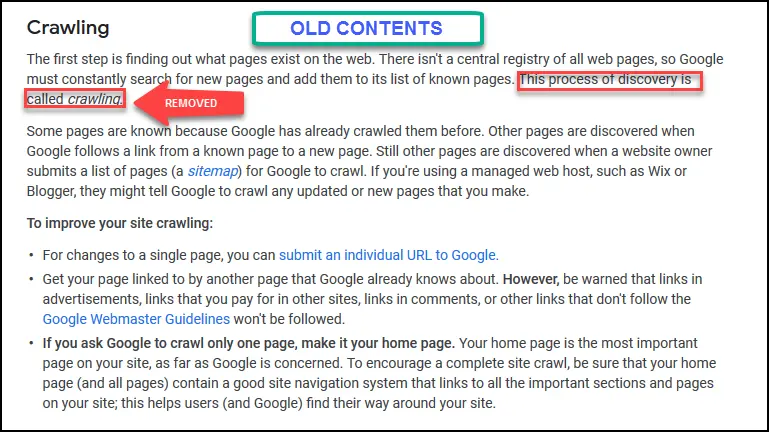
This is the crawling section of 07th June (older version).
What’s New In Crawling?
Google has mainly tried to provide more clarity on its crawling process for webmasters.
“Once Google discovers a page URL, it visits, or crawls, the page to find out what’s on it. Google renders the page and analyzes both the text and non-text content and overall visual layout to decide where it should appear in Search results. The better that Google can understand your site, the better we can match it to people who are looking for your content.”
So Google crawls pages and analyzes textual and non-textual content (images, videos etc.) and overall visual layout to decide about its search appearance. Here overall visual layout might be indicating various ranking factors like page design, whitespace, above the fold issue, readability and other UX issues.
New Advises For Webmasters To Improve Site Crawling:
Google has advised the following new things to webmasters to improve their site crawling:
- Allow Google bot to access all the images & section of your pages so that it could understand the page context properly.
- Use sitemap to inform Google about many new or updated pages.
- For smaller sites with less than 1000 pages, make Google aware about only your home page with proper site navigation so that Google could crawl all your pages.
New Contents in The Long Version:
In the crawling section, Google added;
“During the crawl, Google renders the page using a recent version of Chrome. As part of the rendering process, it runs any page scripts it finds. If your site uses dynamically-generated content, be sure that you follow the JavaScript SEO basics.”
We know Googlebot can crawl Java Script, not skip them anymore. So, webmasters should follow the SEO guidelines for Java Script.
Primary crawl / Secondary crawl
Google added here a new concept of primary crawl and secondary crawl. So far we’ve heard about desktop crawler and mobile crawler. After mobile first indexing, this concept of primary crawl and secondary crawl came into picture.
Here is the newly added content.
“Google uses two different crawlers for crawling websites: a mobile crawler and a desktop crawler. Each crawler type simulates a user visiting your page with a device of that type.
Google uses one crawler type (mobile or desktop) as the primary crawler for your site. All pages on your site that are crawled by Google are crawled using the primary crawler. The primary crawler for all new websites is the mobile crawler.
In addition, Google recrawls a few pages on your site with the other crawler type (mobile or desktop). This is called the secondary crawl, and is done to see how well your site works with the other device type.”
So basically, mobile crawler or desktop crawler, anyone of these can be the primary crawler for your site. But for all new websites, mobile crawler is the primary one. Google runs a secondary crawl of few pages with the other crawler.
So, what is the difference you might ask. Well,
With primary crawler, Google crawls your entire website but with the secondary crawler, it crawls a few pages.
That means primary crawler helps Google to index and understand your website and that defines your fate in search appearance. Secondary crawler helps Google to decide how your pages could be appeared in search results in that type of devices.
In the long version, 2 new points were added in Improve your crawling section.
- Be sure that Google can access the key pages, and also the important resources (images, CSS files, scripts) needed to render the page properly.
- Confirm that Google can access and render your page properly by running the URL Inspection tool on the live page.
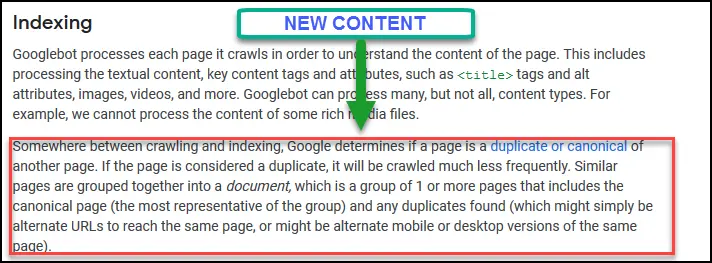
And here is the only new content in the indexing section which tells about crawling & indexing of duplicate or canonical pages.
Google has added a special note on What is a “document?” which describes about the canonical or duplicate page issues and how Google considers it. Few important points we’re adding below:
- Each document represents one or more identical or similar webpages having same content.
- Google selects one URL of the document as the canonical URL and crawls and indexes it.
- The duplicate or alternate URLs are also sometimes crawled by Googlebot.
If a document’s canonical URL is a mobile URL, Google will still serve the alternate URL (Desktop URL) for users searching on desktop.
- Do SEOs Need To Know HTML? - December 20, 2021
- How To Find Attribution-Free Music For Your Videos? - September 20, 2021
- OpenAI Codex – Future Of Software Development In Automation - August 12, 2021